- Home
- Blog
- Digital dentistry
- Orthodontic software
Orthodontic software for patient engagement and digital precision
What is orthodontic software used for?
Orthodontic software is a term for a range of digital applications the doctor runs on their computer to plan and follow treatment. It connects with dental hardware such as CBCT or intraoral scanners and helps dental specialists with orthodontic treatment planning, and designing appliances for teeth alignment, for example. Dental software solutions help the dentist work backwards from the desired treatment outcome and predict how the different stages in treatment are best planned. The main goal is to reach the treatment result as accurately and timely as possible.
Speaking generally, there are three types of orthodontic software, each serving different needs:
- Software to generate 3D digital models on screen.
- Software for orthodontic treatment simulation.
- Software for analysis and treatment planning.
An orthodontic digital workflow could be using all three solutions after one another, or the workflow could require only using one or the other, depending on the need. Below we will describe the difference.
3D digital modeling software
This is software that comes with a scanner and ensures that the scanner can generate a 3D model of the oral cavity. When the 3D file is created, the software will allow for the file to be shared with visualization and orthodontic treatment software, or with external collaboration partners.
Scanner software for digital orthodontics cases doesn’t necessarily require advanced proficiency in digital dentistry. It is rather the other way around: if the scanner software is built in the right way, it makes scanning for orthodontic cases smooth, quick and with the right data quality.
Scanners these days for example utilize technology like machine learning or Artifical Intelligence to ensure the scanner can distinguish textures and colors in the right way, which helps the dental expert prepare the file for further processing more quickly.
Orthodontic treatment simulation software
Orthodontic software for treatment simulation is a possible next step in the workflow if the doctor intends to utilize visualization tools to communicate with the patient. Software to simulate bracket or clear aligner treatment works similar to smile simulator solutions; all the doctor needs is a 2D image, the scan and the software with additional technology.
The collaboration between IvoSmile and 3Shape for example, uses augmented reality for real-time visualization while the patient is in the chair. While the patient is consulting their doctor about an esthetic dental makeover, the doctor can project treatment outcome in 3D on a ‘virtual mirror’. The live patient images on an iPad or iPhone show the patient’s future smile. Technological possibilities such as these create easy and powerful communication and it tends to help with treatment acceptance.
Analysis and treatment planning software
When the doctor is ready to initiate the next step, we get to the category of 3D orthodontic software solutions.
This includes for example clear aligner design software or software to help with bracket placement. Clear aligners are one of the fastest-growing options for teeth alignment in dentistry.
Offering clear aligner treatment to patients has become much easier by digitizing (parts of) the workflow. The impression taking process can for example be digitized so that the starting point of the design and production process is digital already.
Working with digital models in orthodontics offers numerous advantages in terms of storage space 1. Grauer D, Cevidanes LH, Tyndall D, Styner MA, Flood PM, Proffit WR. REGISTRATION OF ORTHODONTIC DIGITAL MODELS. Craniofac Growth Ser. 2011;48:377-391. PMID: 26549917; PMCID: PMC4636130., spatial registration and superimposition, and can also solve hygiene and accuracy problems encountered with conventional plaster study models 2. Matthew J. Peluso, Stuart D. Josell, Sam W. Levine, Brian J. Lorei. Digital models: An introduction. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sodo.2004.05.007. The intraoral scanners accuracy that they bring into the game, also allows for dentists to track changes over time and analyze them with digital precision.
Designing and planning aligner treatment is done with clear aligner software. This type of dental aligner software can be used either by the clinic to design the treatment in-house or by the lab. Dental aligner software saves time and increases efficiency because it automates many of the steps. While the software is doing the auto segmentation, wax-up and hollowing of models, the doctor can do other things. One important element to keep in mind when using orthodontic software for aligners is whether the workflow is an open or a closed one: an open workflow gives possibilities for collaboration with various aligner providers — a closed workflow limits the patient’s options to a singular brand.
Outside of orthodontic software for aligners, there are also other types of orthodontic planning software on the market to help with creating customized digital analysis, and plan and share different types of orthodontic treatments.
When the case is planned, the production phase in the workflow can also be catered for in a digital way. The treatment plan can be shared between dental clinics and labs or other dental solutions providers. At the end of the day, it is up to the doctor to decide if they go for producing clear aligners in-house with orthodontic 3d printing software, send the case to the lab or if they will send it to third parties.
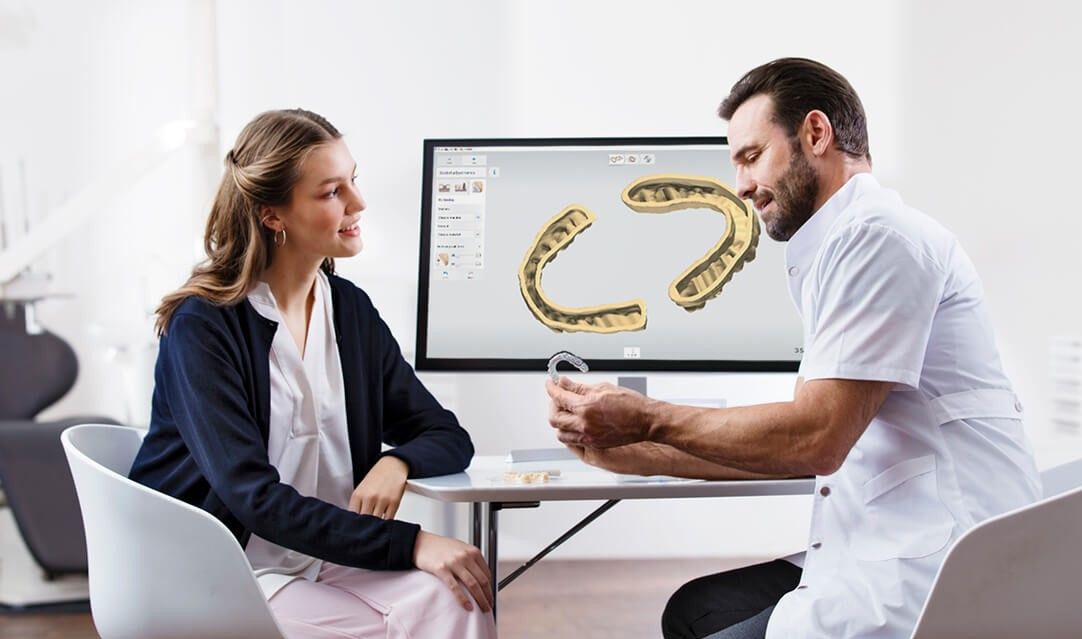
Benefits of orthodontic software for clear aligners
Digital orthodontic treatment solutions are generally seen as good ways to involve patients and make the treatment process more comfortable and efficient. It is also a good way to start offering new treatment types to the practice. With orthodontic CAD/CAM software it is easy to collaborate with partners — who can do parts of the workflow that the doctor cannot do themselves. More benefits of performing orthodontic treatments digitally:
- Analysis tools let dentists take into account all possible nuances while analyzing cases and planning treatment, and provide a more accurate diagnosis.
- Digital precision of intraoral scans and orthodontic software help to provide accurate treatments with good fit.
- A digital workflow combines different software and hardware solutions, which makes the collaboration with new partners easy. Some types of orthodontic software for clear aligners, for example, are set up so that the doctor can directly connect to a clear aligner provider of choice.
- Realistic simulations that are shareable make it easy to achieve patient engagement.
- Digital solutions give better insight into complicated surgical-orthodontic cases (with severe dentofacial problems, for instance) 3. Vig KD, Ellis E 3rd. Diagnosis and treatment planning for the surgical-orthodontic patient. Dent Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;34(2):361-84. PMID: 2186939..

Resources
- Grauer D, Cevidanes LH, Tyndall D, Styner MA, Flood PM, Proffit WR. REGISTRATION OF ORTHODONTIC DIGITAL MODELS. Craniofac Growth Ser. 2011;48:377-391. PMID: 26549917; PMCID: PMC4636130.
- Matthew J. Peluso, Stuart D. Josell, Sam W. Levine, Brian J. Lorei. Digital models: An introduction. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sodo.2004.05.007
- Vig KD, Ellis E 3rd. Diagnosis and treatment planning for the surgical-orthodontic patient. Dent Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;34(2):361-84. PMID: 2186939.